Topics & EventSee More
-
【Press release】Unveiling the Molecular Functions of Lipid Droplet Proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana LeavesLipid droplets (LDs) serve as storage organelles found in plant l...2024/04/24(水)
-
The schedule of entrance examinations for the fiscal year 2024 has been updated.Please click here2024/04/03(水)
-
Information on the May 2024 Chiba University Graduate School of Horticulture Admission Guidance Fair has been updated.Please click here2024/04/03(水)
-
Graduate Student in the Department of Horticultural Science, Fawibe Kehinde, Wins Best Presentation Award at International Conference!Graduate student Fawibe Kehinde (referred to as Kenny) enrolled i...2024/03/20(水)
-
An article introducing Associate Professor Ryosuke SHIMODA was published in CHIBADAI NEXT.An article introducing Assoiate Professor Ryosuke SHIMODA was pub...2024/02/15(木)
-
An article introducing Associate Professor Akira KATO was published in CHIBADAI NEXT.(2023/9/12)An article introducing Associate Professor Akira KATO was publish...2024/02/14(水)
-
An article introducing Professor Hideyuki TAKAHASHI was published in CHIBADAI NEXT.(2023/10/20)An article introducing Professor Hideyuki TAKAHASHI was published...2024/02/14(水)
-
An article introducing Professor Masashi NOMURA was published in CHIBADAI NEXT.(2023/10/30)An article introducing Professor Masashi NOMURA was published in ...2024/02/14(水)
-
Web site renewal.Web site renewal.2024/02/09(金)
Introduction
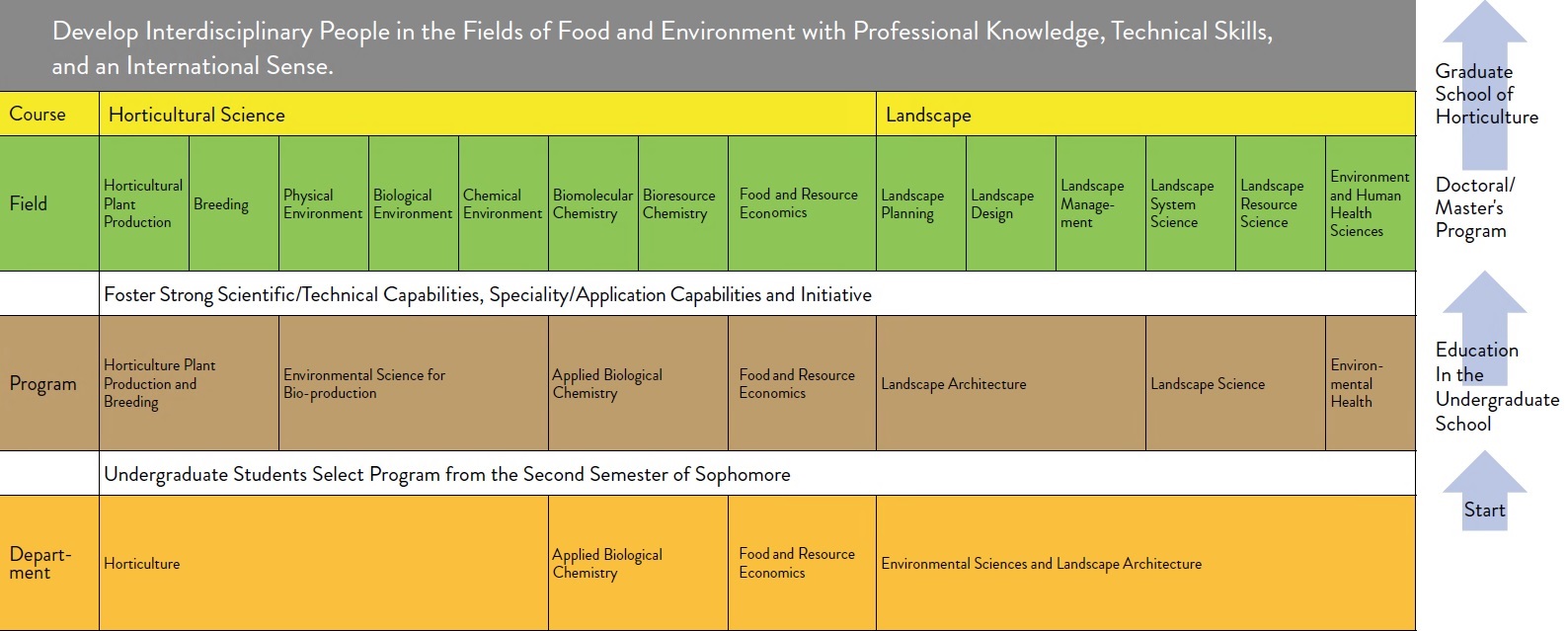
The Chiba University Graduate School of Horticulture, Faculty of Horticulture, is the only school of its kind among Japanese universities. The School aims to produce integrated solutions for international challenges in the areas of food production, the environment, human health, energy and resources, as well as to foster internationally recognized professionals in these areas. As part of its objective to foster personnel who can work on an international stage, the School offers seven undergraduate programs across four departments as well as two graduate courses encompassing fourteen fields. With this structure, the School is determined to raise community awareness of the distinctive research areas that it has worked to develop, along with their potential for further expansion in the future.
History
- 1909 Founded as the Chiba Prefectural Technical College of Horticulture
- 1929 Transferred to the control of the former Ministry of Education, becomes the Chiba Higher College of Horticulture
- 1949 Becomes the Faculty of Horticulture of Chiba University
- 1969 Master's program for the Graduate School of Horticulture established
- 1988 The Graduate School of Science and Technology (a Doctoral program) established
- 2007 Following a reorganization of the Faculty of Horticulture and the Graduate School, the Graduate School of Horticulture established
Graduate School of Horticulture
Guiding Education Principles
The Graduate School of Horticulture is the only specialized graduate school in Japan with a focus on horticulture and landscape, and conducts comprehensive education and research with one Division of Environment and Horticulture. In addition, we will foster human resources with high problem-solving skills through a transdisciplinary approach that takes advantage of the comprehensiveness of Chiba University.
The traditional principle of the education and research in Graduate School of Horticulture is "Theory and Practice", which emphasizes theoretical considerations of problems and values practice based on the scientific approaches. Practice also refers to the verification of research results in the social and industrial realities, but the reflections obtained there will be the next scientific opportunity. Through such processes, we train professionals with advanced knowledge and creativity.
The other principle is the development of internationality. In modern society, information and transportation have no borders. Science is evolving day and night as people around the world compete. On the other hand, social problems occur in specific areas and sites, and it is important to scoop them up and work on solving them. Think globally, act locally! We develop human resources who can consider so deeply and act lightly.
Curriculum
The Division of Environment and Horticulture consists of three courses, Course of Horticultural Science, Course of Landscape and International Course of Environmental Horticulture, each of which has a curriculum consisting of basic courses and three specialized courses.
Master's program is programed as follows.
In basic course, subjects related to our educational policy of "The spirit of freedom and independence" must be taken. Those subjects is professional ethics and researcher ethics. In addition to the required subject, this course offers academic writing subjects and international relations subjects related to "Involvement in society on a global perspective". These will be selected as required courses, and students will acquire specialized and applied communication skills through seminars and research.
Specialized courses are provided to acquire "Specialized knowledge, technology and skills". Of these, required compulsory course is the common specialized course of the program. This course shows a sketch of professionalism, understand the academic and social positioning of research and learning, and acquire their own research development, science and technology management abilities, and policy-making abilities.Compulsory elective course is at the core of the specialized curriculum and provide lectures on advanced knowledge and the latest methodologies in each specialty. We will set the minimum number of required credits for each course to ensure a balanced learning.
Elective course is set for two purposes. The first purposes is to provide advanced students from other universities and students who want to expand into new areas at graduate schools the expertise they need to base their elective courses. The second purposes is to broaden your area of specialization and to select a wide range of courses to gain the knowledge and abilities to discover and solve problems from a broad perspective.
Seminars and studios are set up as subjects for fostering "Excellent problem-solving skills", and students acquire inquiring skills through graduate research.
Doctoral program is programed as follows.
Basic courses are environmental horticulture technology management and environmental horticulture entrepreneur training courses related to "The spirit of freedom and independence". In order to foster human resources who can conduct autonomous research and development and transmit their results internationally and interdisciplinary, seminar-type courses related to international academic development or management are set as common courses.
Regarding specialized courses, students are able to voluntarily take a wide range of subjects required for research development.
In order to develop the problem-solving skills, we will secure sufficient research time, provide opportunities for joint research through industry-academia-government seminars and provide appropriate guidance individually through graduate seminars.
(1) Course of Horticultural Science
Graduate studies of Horticultural Science offer four programs: i.e. Horticultural Plant Production and Breeding, Environmental Science for Bioproduction, Applied Biological Chemistry, and Food and Resource Economics, leading to Master's and Doctoral degrees. The Master's Program provides essential education and various research opportunities in the areas of biological production, bioresource management, and economics. On the basis of the Master's program, the Doctoral Program offers interdisciplinary subjects, training to meet international standards, and education for scientific ethics. These programs build up expertise of a candidate not only in the research and development of bioresources, and food economy but also in the practical skills to achieve internationally with high ethical standards.
(2) Course of Landscape
Aiming at the reconstruction of ecological space and sustainable society, the Course of Landscape provides the integrated academic program: both of design of the aesthetical environment and the sciences of ecological system. Students learn wide range knowledge through design to science, while they challenge their own research or creation in each academic division. The course produces the high-profession of design, management, healthcare in landscape field as well as the qualified researcher in the ecological science.
Education and Research Objectives for the Programs
1.Course of Horticultural Science
(1) Horticultural Plant Production and Breeding
This program offers advanced knowledge and skills for plant cultivation and management as well as breeding and genetic engineering techniques of not only horticultural crops but also medical and functional food plants. This program also offers education and research on breeding program and strategy that meet social needs as well as plant cultivation techniques with environmentally sustainable manners for the horticultural plant production. Development of highly skilled engineers and researchers with global view, wide perspective and creativity is also aimed in this program through acquiring practice-based skills and knowledge on areas that overlap the boundaries between related programs.
(2) Environmental Science for Bioproduction Program
This program offers education and research on systematic theory on physical, biological and chemical environmental factors affecting bioresource production such as climate, soils, cultivation facilities and fields for the production of plants; the behavior and cyclings of the bioproducts and substances used in those environments; physiology, ecology, pathology and utilization of cultivated plants; and the insects and microorganisms that inhabit those environments. Through these educational programs, we aim to foster engineers and researchers with enough background of physical, biological and chemical aspects of environmental science, who have the technical capabilities and applied skills to create and control suitable production environments.
(3) Applied Biological Chemistry Program
For the purpose of achieving effective applications of bioresources using animals, plants and microorganisms, students analyze the functions, substances of cell constituents and metabolites of these living organisms using methods in biochemistry and molecular biology. Students also study basic scientific principles and theories of applied technology relating to subjects including related genes, functional proteins such as enzymes both inside and outside cells, functional carbohydrates, and functional lipids. This program fosters professionals who will be able to contribute to solutions for the problems currently facing humanity in areas such as food production, natural resources, and environmental issues.
(4) Food and Resource Economics Program
Based on natural sciences, the course trains the students in analytical tools of social sciences. The targets of the training involve a broader view of the entire systems of food chains, interdisciplinary expertise, and leadership to promote policy makings. Managing a variety of resources in rural societies, conserving the environment, and sustainable developments under the globalized economy are essential, also. The course brings up human resources to solve the related problems proactively.
2.Course of Landscape
(1) Landscape Planning Program
Focusing on cities, rural communities and natural areas, students interpret the contradictions that occur between the daily lives of people in those areas and the spaces and natural environments that support those lives. Students also investigate both the direction of their development as well as the plans, systems and methods for realizing the comfortable and ecological living environment. The spaces principally examined range from urban spaces such as town precincts and pedestrian walkways to wilderness areas such as national parks, mountains and forests. Spaces also include residential places such as small towns and villages and rural spaces such as farming communities.
(2) Landscape Design Program
Students undertake research on open spaces ranging from private gardens to urban-scale spaces from the perspectives of history, community and culture in order to deepen their examination of the design of open spaces as environmental facilities. Specifically, students analyze and interpret the structure of spaces, including historical gardens in Japan and overseas, gardens in private homes, public parks, and open spaces in residential areas. Students also research landscape systems and policy theories. Based on this research students investigate the planning, design methods and cultural context of those particular open spaces that modern communities regard as useful.
(3) Landscape Management Program
This educational research program deals with fundamental theories, applied technologies, and policies for appropriately managing different kinds of green spaces: planting sites, historical gardens, community gardens, urban parks, natural green spaces, and the local environment in which they exist.
The program aims to develop a sustainable community and local environment to regenerate the environment and reduce environmental load, based on the multiple roles of green spaces.
By educating the students and through research activities, we aim to contribute to resolving various social issues such as rebuilding the relationship between people and nature, understanding and appropriating local culture and traditions, cultivating communities, creating lively towns, reducing and preventing disasters, and adapting to population decline.
(4) Landscape System Science Program
Based on analyses of landscape environments from earth science and ecological perspectives and by studying modeling of those systems, students forecast and evaluate changes to landscaped environments caused by environmental changes such as global warming and urbanization, regional development, and increases in specific biopopulations. Students also investigate and develop techniques for forming sustainable systems appropriate for regional human and ecological environments.
(5) Landscape Resource Science Program
Based on research from biological and ecological perspectives of the animals, plants, soils and water that constitute terrestrial and marine landscaped environments, students study the multiscale synchronic structures, diatonic changes and functional relationships within those environments and investigate and develop skills for using, preserving and recycling landscaped environment resources in specific contexts such as urban beautification and waste land beautification, natural environment assessments, nature remediation, and habitat management.
(6) Environment and Human Health Sciences Program
The issues taken up by this program relate to well-being and health-related issues such as creating better relationships between people and the environment, raising people's QOL (Quality of Life) , mitigating their stress and enabling mental calm, for healthy people alike and not just for those requiring care for an illness or injury. This program's perspectives encompass open spaces and horticulture, medicine, pharmacology, well-being and education, and its education and research extend to: the therapeutic, physical and emotional welfare uses of plants in areas such as horticultural therapies and aromatherapy; the use of elements in nature to beautify medical and welfare facilities; plants as medicinal resources; plant- and environment-based culture; environmental education; and education on and the dissemination of agricultural and environment-related fields.
Faculty of Horticulture
Faculty of Horticulture
"Food, Horticulture and Landscape" are the key words that characterize our department. Faculties with advanced specialist knowledge cooperate in creating a study environment to foster the development of skills and techniques in the production and use of horticultural plant resources, biotechnology, efficient use of resources and energy to reduce environmental impacts, conservation and regeneration of environments where people and nature coexist, creation of landscapes, use of plants that apply concepts of medical science and welfare, and management, marketing and policies of industries related to these. In this way, the course prepares students who are capable of working at the forefront of the field of horticulture internationally and contributing to creating the society of the future.
The faculty adopts an educational program system that provides students with basic skills in a traditional framework and forefront knowledge in the areas of their programs. Through practical sessions in small groups in the areas of specialization, the program fosters the development of flexible skills in setting and resolving issues. The program is linked to the Graduate School of Horticulture where students can smoothly continue to develop their specialist skills further.
Department of Horticulture
The wide and systematic knowledge can support future earth environment
The students will study the cultivation technique, biotechnology and environmental management for plants biologically, physically, and chemically. An expert who has basic and practical knowledge and technique will be trained.
Feature 1 A wide view is trained by two programs
There are two programs [Horticulture plant production and breeding] and [Environmental Science for Bio-production].
An expert who has basic and practical knowledge and technique with specialized knowledge for cultivation technique, breeding, environmental (biological, physical and chemical) factors will be trained.
Feature 2 Horticulture Plant Production and Breeding
Students will study the cutting-edge cultivation and breeding knowledge and technique, and biotechnology. In addition, education and research on protected horticulture will be also performed
Feature 3 Environmental Science for Bio-production
Students will study environmental Science for bio-production, based on the knowledge of biological, physical, and chemical environmental factors. In addition, education and research on climate, soil, nutrition, disease, insect and so on will be also performed.
Department of Applied Biological Chemistry
We will try to solve various problems by clarifying biological functions using biological and chemical methods.
Students will study comprehensively about the functions of organisms, properties of cell components and metabolites in order to make effective use of life resources using microorganisms, plants and animals. This department aims to develop students who can solve various problems facing humanity, such as food, resources, and environment.
Feature 1 Learning comprehensive knowledge
Students can learn basic academic ability related to biochemistry and food chemistry, microbiology, molecular biology, organic chemistry with the keywords, "Life, Food and health, Biomass, and Environment". Students who will go on to graduate school are trained to be act as bioscience researchers in the future.
Feature 2 Education to develop applied ability.
We teach and nurture technical knowledge, skills, and its application ability for students who are willing to explore various functions of living organisms at the molecular, cellular, individual or community level. This program aims to develop human resources who are motivated and capable of contributing to society.
Feature 3 Aiming for effective use of biological resources
We will explore and discover novel useful creatures and biologically functional molecules, and clarify their biological characteristics. We will also investigate mechanisms of functional expression of these organisms and molecules using biochemical and molecular biological methods. This department will respond to further social demands through such research.
Department of Environmental Sciences and Landscape Architecture
Aiming to preserve and create a comfortable ecological environment
Learn the theory and practice to create a necessary environment where people can live comfortably in harmony with nature. The students can understand approaches and techniques for elucidation of the natural ecological processes, conservation and regeneration of the natural environment, utilization and management of green space, the cultural history of the environment, and the utilization of greenery for mental and physical health.
Feature 1 Landscape Architecture Program
This course focuses on space formation and management techniques and theories that integrate the natural and cultural aspects of the green space environment. Train engineers who can plan, maintain, manage, and operate the environment where people and nature coexist in harmony, while planning and maintaining green spaces such as city gardens and parks, as well as rural areas, and protecting the natural environment.
Feature 2 Landscape Science program
Students learn theories and technology of the green space environment comprehensively in the natural science aspects, which includes the green space environmental systems and modeling, engineering technologies related to green space-forming, as well as creation and management of green space. Students can use the theories and technology to research the green space environment based on the fieldwork of biology and geosciences.
Feature 3 Environmental Health Program
Students learn theories and technology of horticultural therapy and aromatherapy associated therapeutic and welfare plants, greening of medical welfare facilities, medicinal resource plants as well as environmental education. Using knowledge and technology about green space environment, horticulture, as well as health and therapy, the student can build better relationships between people and the environment through QOL improvement and stress reduction.
Department of Resource and Environmental Economics
We aim at developing human resources that are well-acknowledged with food systems consisting of production, distribution, and consumption.
They are capable of planning and evaluation of policy measures regarding the environment, agriculture, and regional development. Besides, they can solve the problems relating to the above issues based on agronomy and social sciences.
Feature 1 Training of problem-solving ability
Based on social science theories such as economics and marketing theory,
We have students acquire the ability to analyze and consider issues, including food and agriculture problems, biological resources, the environment, and even the food industry in Japan and overseas. We also aim to develop human resources with specialized knowledge focused on specific areas in those issues.
Feature 2 We provide students with a balanced scientific sense.
Recent issues on food and natural resources are complex and require a multifaceted approach. We offer programs that are not only analytical methods such as social science and statistics, but also the basics of related natural sciences, and the provide programs that enhance the ability to think about the phenomenon from a balanced perspective.
Feature 3 For a sustainable society
Environmental destruction, food safety, resource management, stable supply of food, etc. are important issues that must be solved to realize a sustainable society.
In this program, students learn about the role and significance of food and agricultural resources and the environment in modern society, and train students to take effective action by using their social science knowledge about the contribution and the role of individuals for society.
Self-introduction on research topics (or My research activities)